Bonds In Brickwork Presentation
| Introduction to Bonds in Brickwork | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bonds in brickwork refer to the arrangement and pattern of bricks in a wall. A well-designed bond provides structural integrity and aesthetic appeal to the brickwork. Different bond patterns offer varying levels of strength, stability, and visual interest. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Common Types of Bonds | ||
|---|---|---|
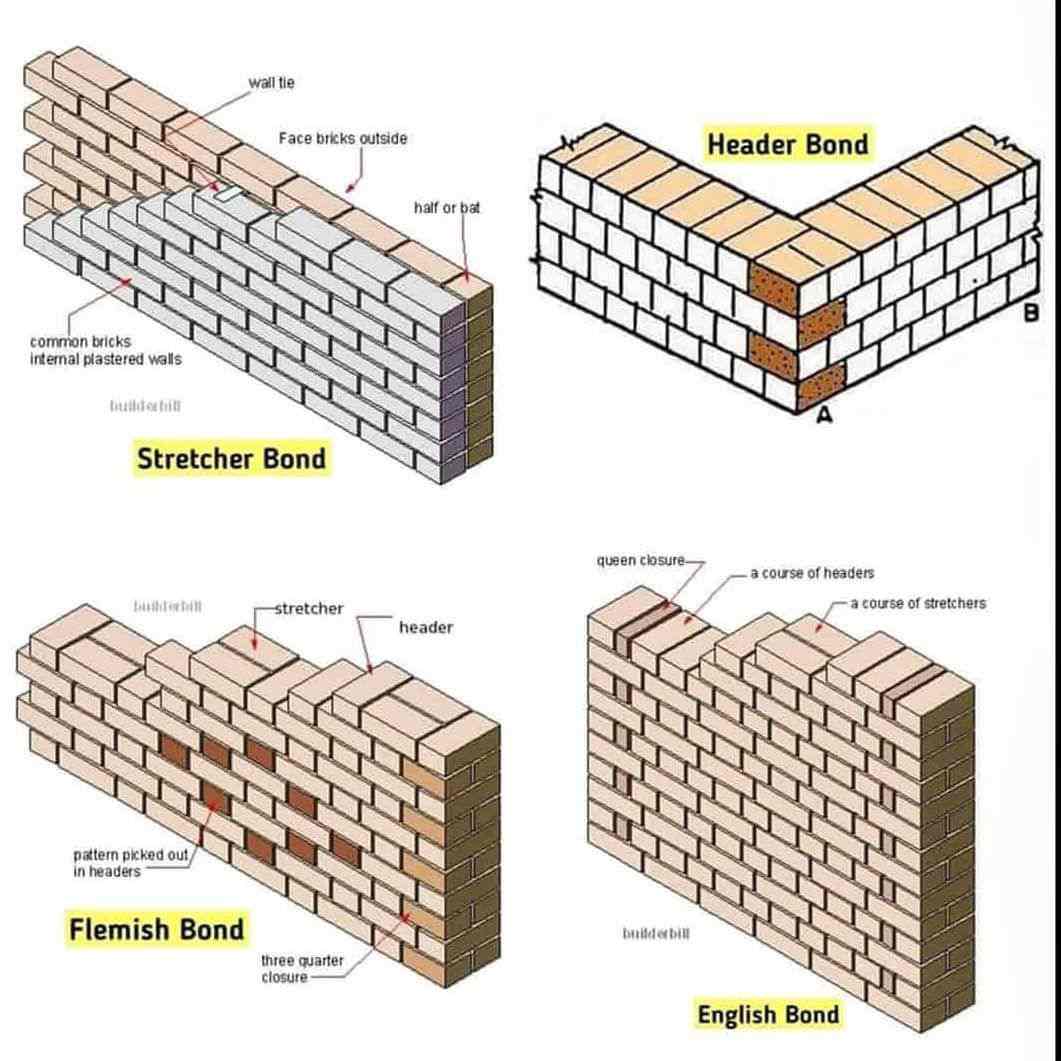
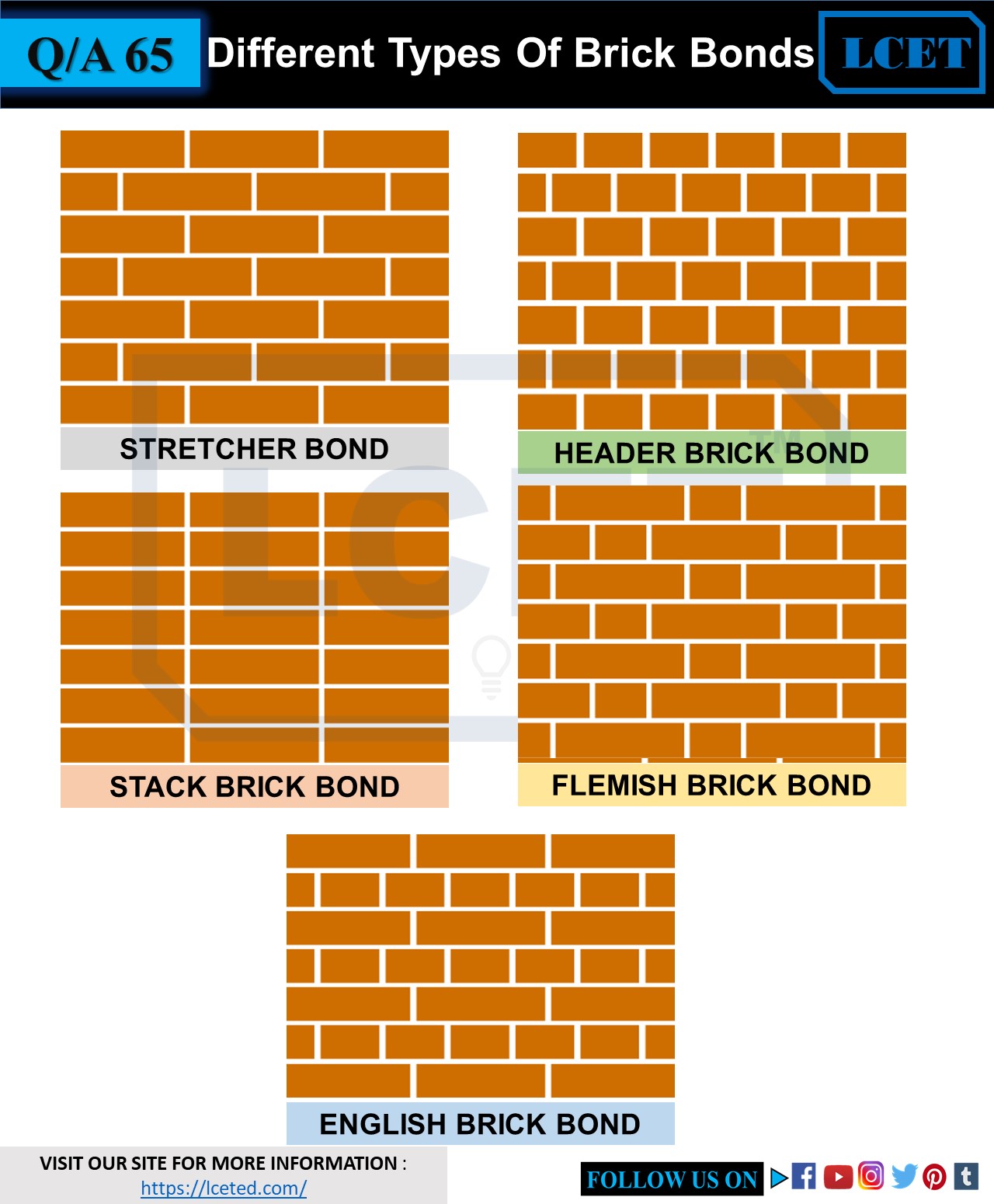
| Stretcher Bond: The most basic and commonly used bond, where bricks are laid lengthwise with their long sides facing outwards. English Bond: Consists of alternate courses of headers (bricks laid with their short sides facing outwards) and stretchers. Flemish Bond: Features alternating headers and stretchers within the same course, creating a more visually pleasing pattern. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Reinforcing Bonds | ||
|---|---|---|
| Header Bond: Used in thick walls or where bonding is required, headers are placed at regular intervals to strengthen the wall. Garden Wall Bond: Similar to header bond, but with additional stretchers in between headers for increased stability. Rat Trap Bond: Utilizes a series of interconnected cavities formed by bricks laid on edge, providing better insulation and reducing material usage. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Decorative Bonds | ||
|---|---|---|
| Stack Bond: A simple, modern bond where bricks are stacked directly on top of each other. Diagonal Bond: Bricks are laid diagonally to create a visually appealing pattern, often seen in decorative features. Herringbone Bond: Bricks are laid at a 45-degree angle, forming a distinctive V-shaped pattern. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Factors Affecting Bond Selection | ||
|---|---|---|
| Structural Requirements: The bond pattern must meet the necessary strength and stability requirements for the wall. Design Intent: The chosen bond should complement the architectural style and desired visual effect. Availability of Materials: Some bond patterns may require specific brick sizes or shapes, which should be considered during selection. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Importance of Proper Bonding | ||
|---|---|---|
| Proper bonding ensures the stability and durability of the brickwork, reducing the risk of structural failures. It helps distribute loads evenly across the wall, preventing cracks and improving the overall strength. A well-executed bond enhances the aesthetic appeal of the brickwork, adding character and value to the building. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Bonding Techniques | ||
|---|---|---|
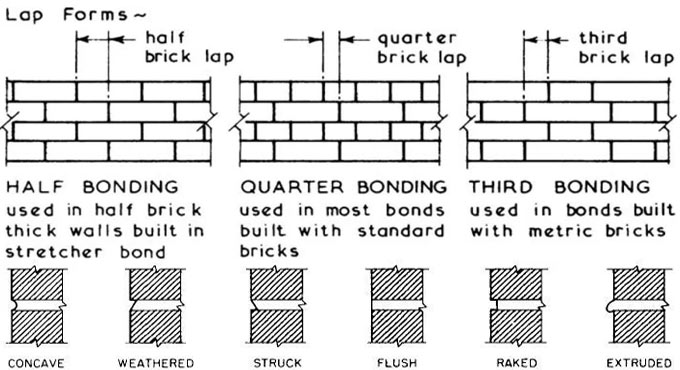
| Mortar Joints: The mortar between bricks plays a crucial role in bonding, providing strength and cohesion to the wall. Bed Joint Reinforcement: Used in areas prone to movement or stress, such as corners and openings, to enhance the bond's durability. Damp-Proof Courses: Integrated within the bond to prevent moisture penetration and protect the brickwork from dampness. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bonds in brickwork are essential for both structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. The choice of bond pattern depends on factors such as function, design, and material availability. Proper bonding techniques and attention to detail contribute to long-lasting, visually pleasing brickwork. | ||
| 8 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Brick Development Association. (n.d.). Bo... Dobson, W., & Warwicker, C. (2005). Brickwork... Chudley, R., & Greeno, R. (2016). Constructio... |  | |
| 9 | ||

/masonry-brick-bond-common-types-2736655-cf1ec5c2e3fe46ad83252d6dbb551a20.png)