Blockchain Technology And It's Applications Presentation
| Introduction to Blockchain Technology | ||
|---|---|---|
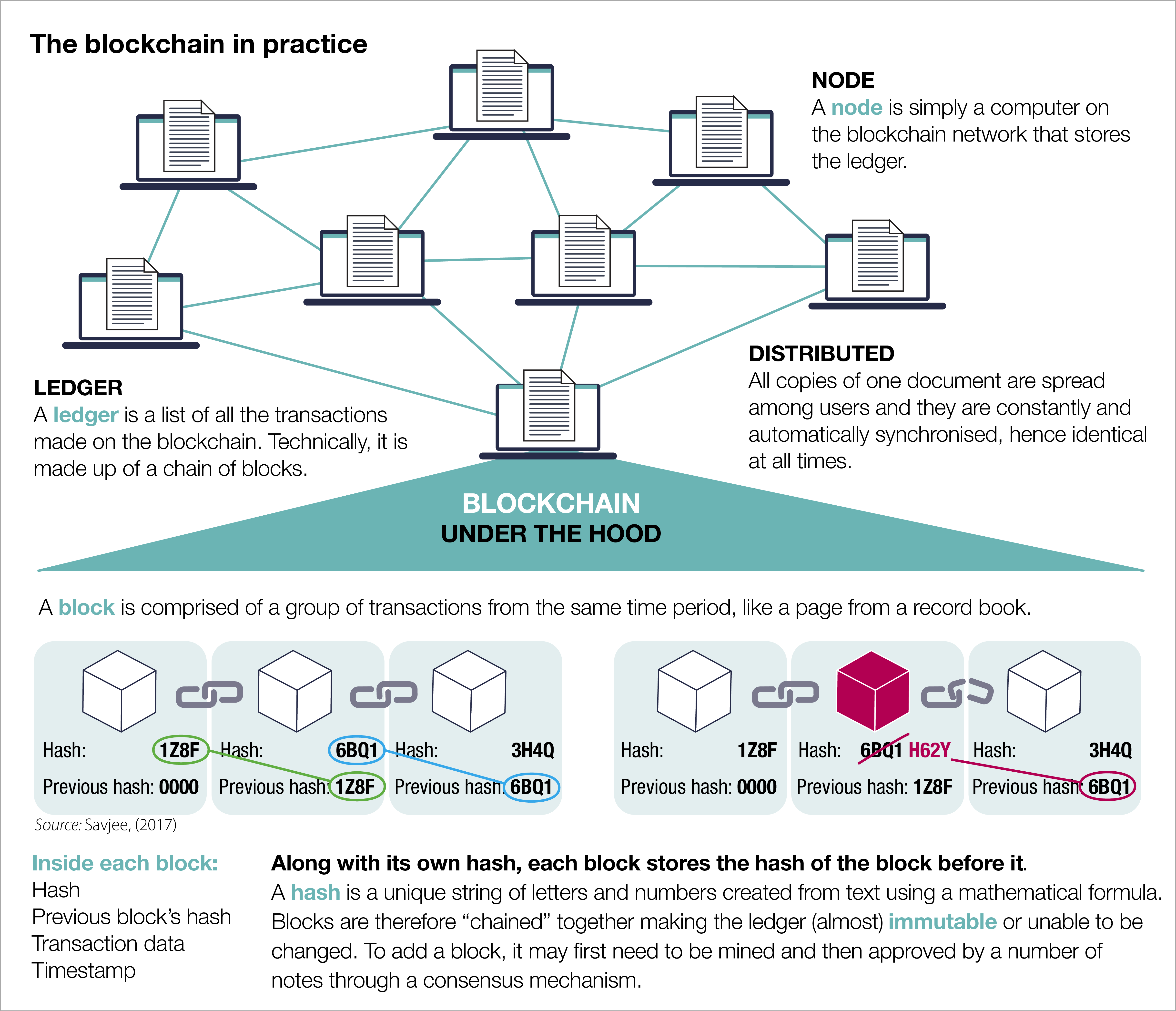
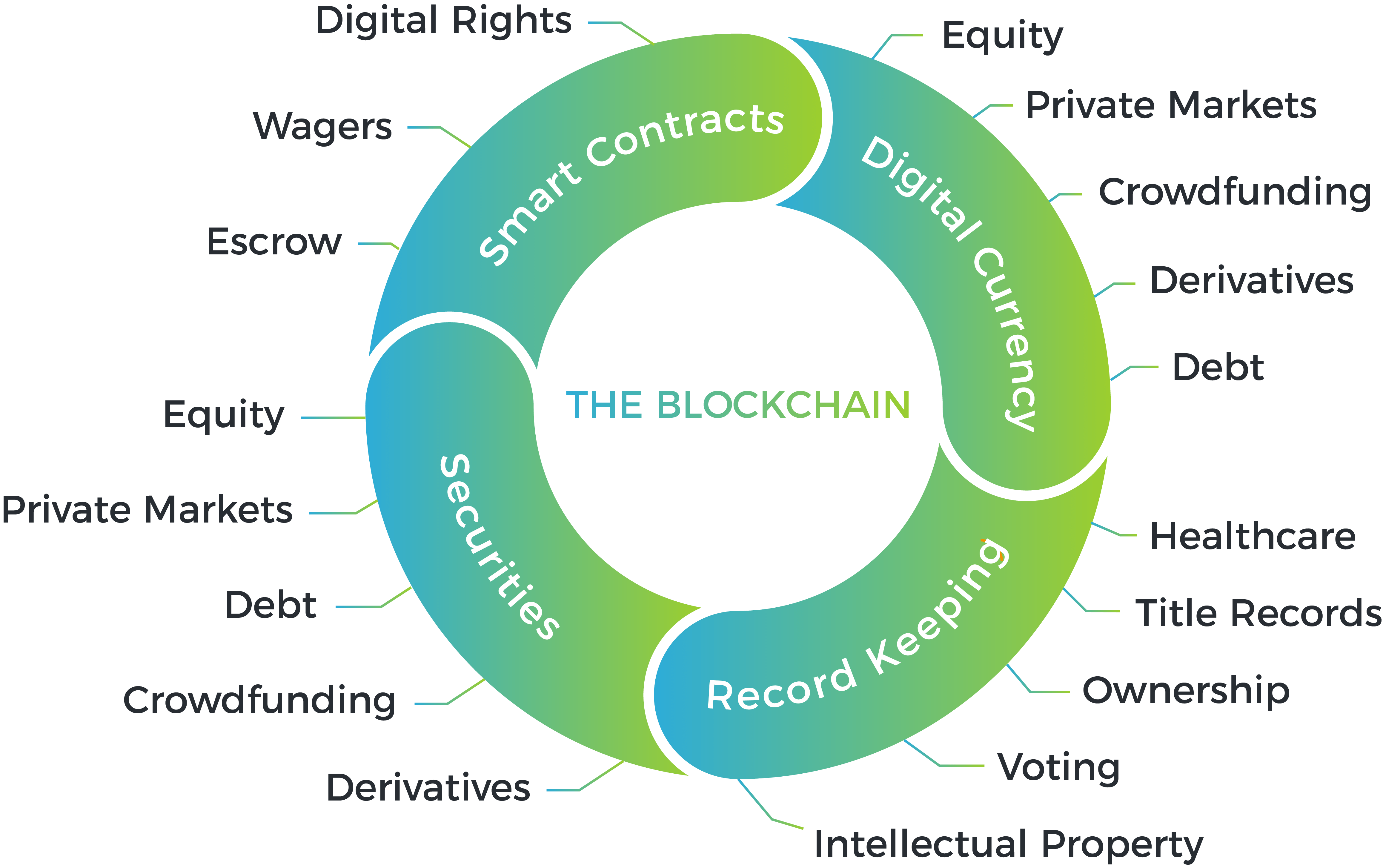
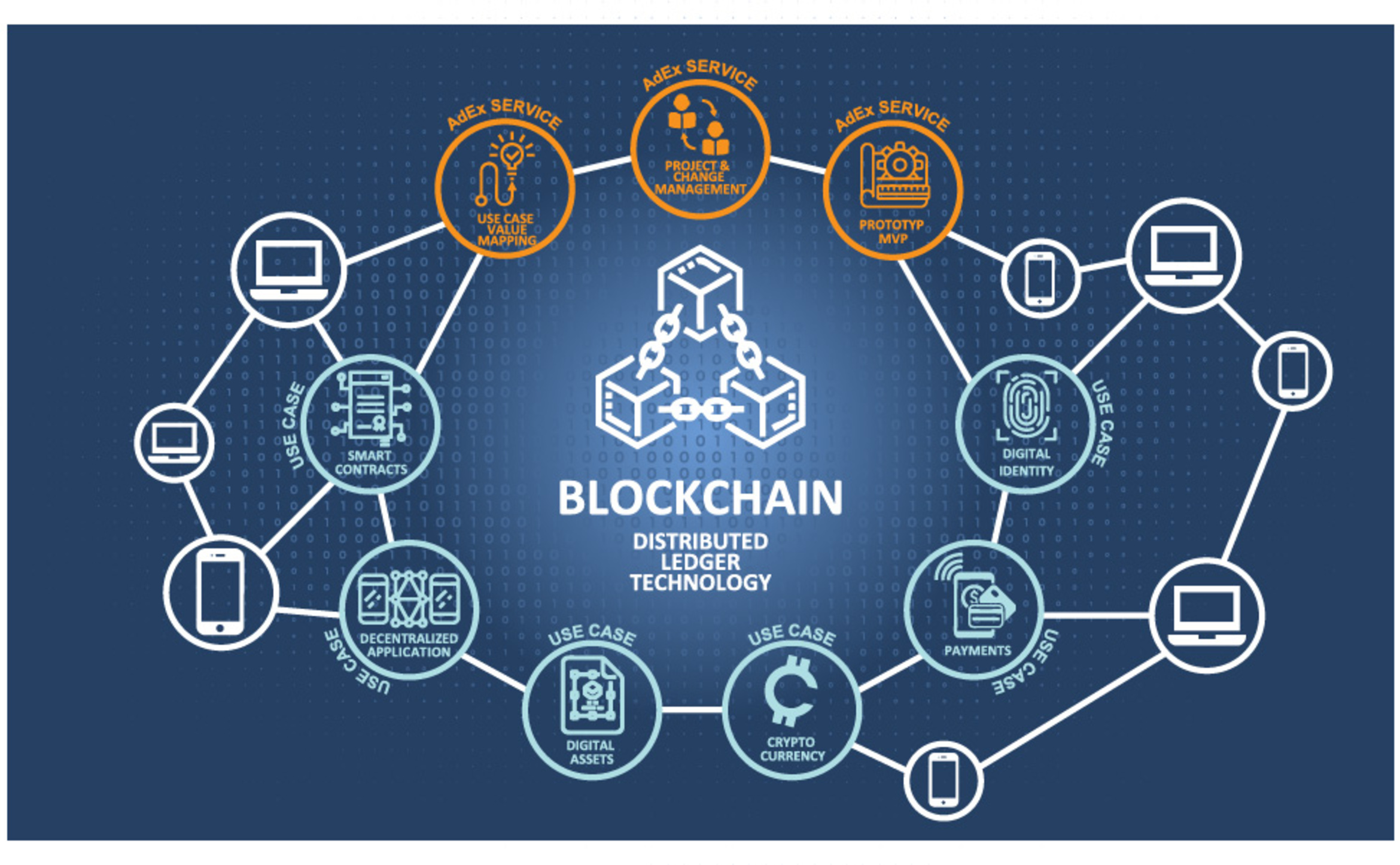
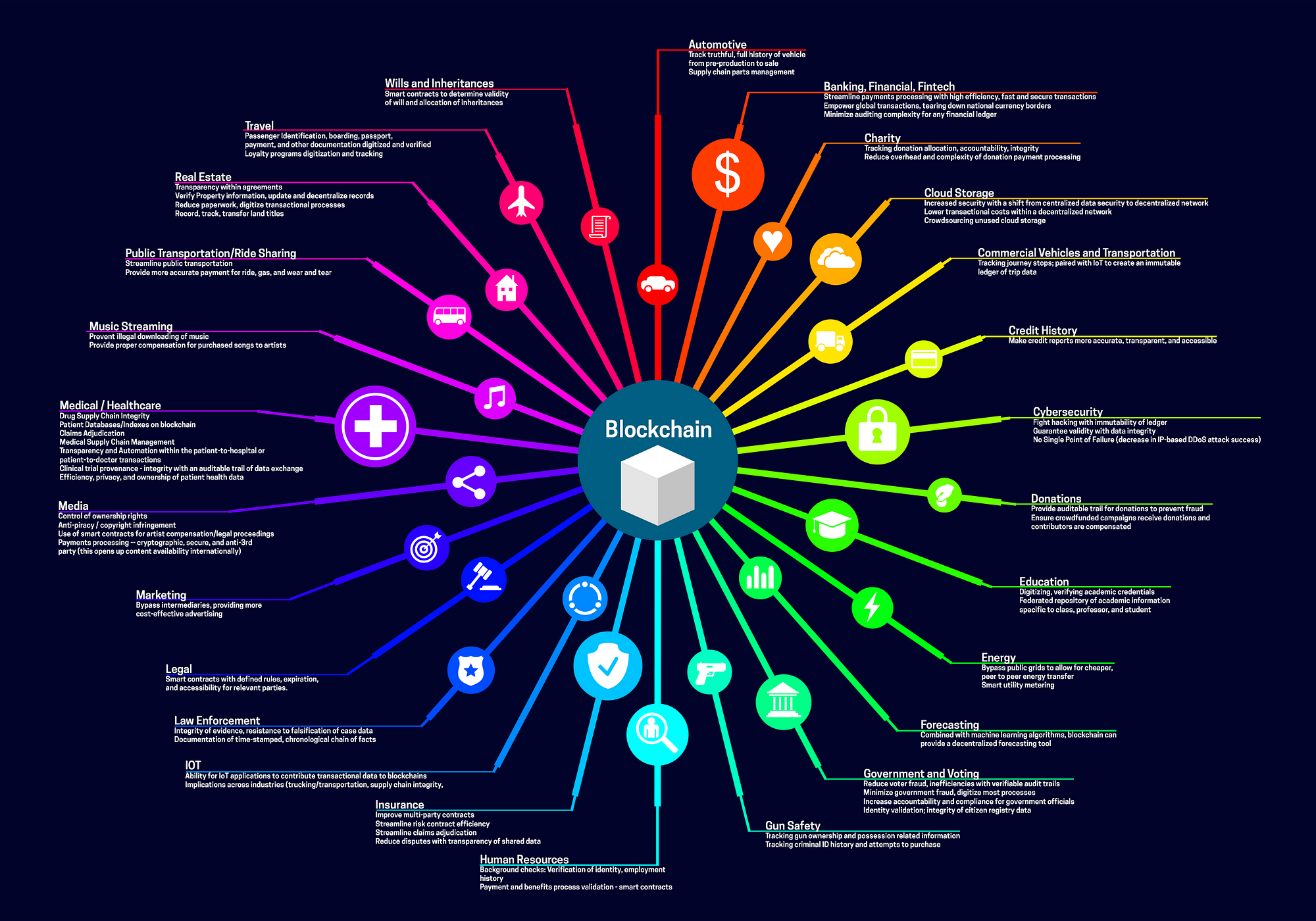
| Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that securely records transactional data across multiple computers. It provides transparency, immutability, and security, making it suitable for various applications. Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries and enhances trust among participants. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Financial Applications of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain enables faster, more secure and cost-effective international money transfers. It can revolutionize supply chain finance by improving transparency and reducing fraud. Smart contracts on blockchain automate financial transactions, ensuring accuracy and efficiency. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Healthcare Applications of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain can securely store and share medical records, ensuring privacy and interoperability. It improves the traceability of drugs, reducing counterfeit medications and ensuring patient safety. Blockchain-based telemedicine platforms enable secure and direct interactions between patients and healthcare providers. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Supply Chain Applications of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency by tracking and verifying the movement of goods. It can prevent counterfeit products by recording every step of the supply chain process. Blockchain ensures the integrity of certifications and origin information, promoting fair trade practices. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Voting and Governance Applications of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain can provide transparent and tamper-proof voting systems, improving the integrity of elections. It enables decentralized governance models where decisions are made collectively and transparently. Blockchain-based identity verification systems can prevent voter fraud and identity theft. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Real Estate Applications of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain facilitates secure and transparent real estate transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries. It enables fractional ownership of properties, increasing accessibility and liquidity in the market. Smart contracts on blockchain automate property transfers and streamline the rental process. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Energy Applications of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain enables peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals to sell excess renewable energy. It enhances transparency in energy transactions, ensuring fairness and preventing fraud. Blockchain-based platforms can incentivize energy conservation and sustainable practices. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Intellectual Property Applications of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain provides a secure and immutable record of intellectual property rights, reducing infringement disputes. It enables creators to directly sell their digital content without intermediaries, ensuring fair compensation. Blockchain can establish provenance for digital assets, preventing unauthorized use and piracy. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain | ||
|---|---|---|
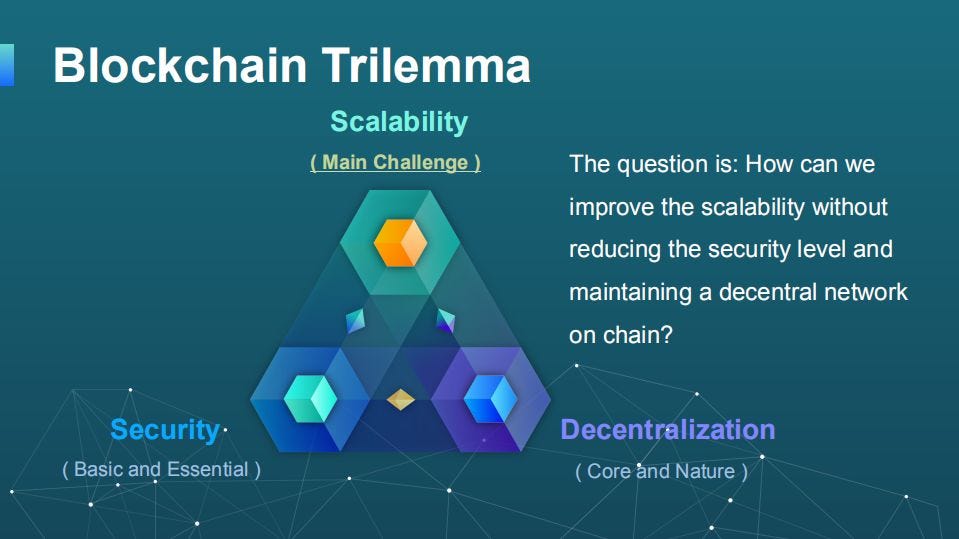
| Scalability remains a challenge as blockchain networks grow in size and transaction volume. Regulatory and legal frameworks need to adapt to accommodate blockchain-based applications. Interoperability between different blockchain platforms is crucial for widespread adoption. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries by increasing transparency, security, and efficiency. Its applications range from finance and healthcare to supply chain and governance. Continued research, development, and collaboration are vital to unlock the full potential of blockchain technology. | ||
| 10 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer ... Swan, M. (2015). Blockchain: Blueprint for a ... Tapscott, D., & Tapscott, A. (2016). Blockcha... |  | |
| 11 | ||