BILLS OF EXCHANGE Presentation
| Introduction to Bills of Exchange | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bills of Exchange are a widely used financial instrument in international trade. They are written documents that allow one party (the drawer) to demand payment from another party (the drawee) at a specified future date. Bills of Exchange facilitate secure and convenient transactions by providing a legal framework for payment obligations. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Features of Bills of Exchange | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bills of Exchange are negotiable instruments, meaning they can be transferred from one party to another. They contain essential information such as the amount of money owed, the due date, and the names of the parties involved. Bills of Exchange can be payable on demand or at a specific future date, offering flexibility for both the drawer and the drawee. | ||
| 2 | ||
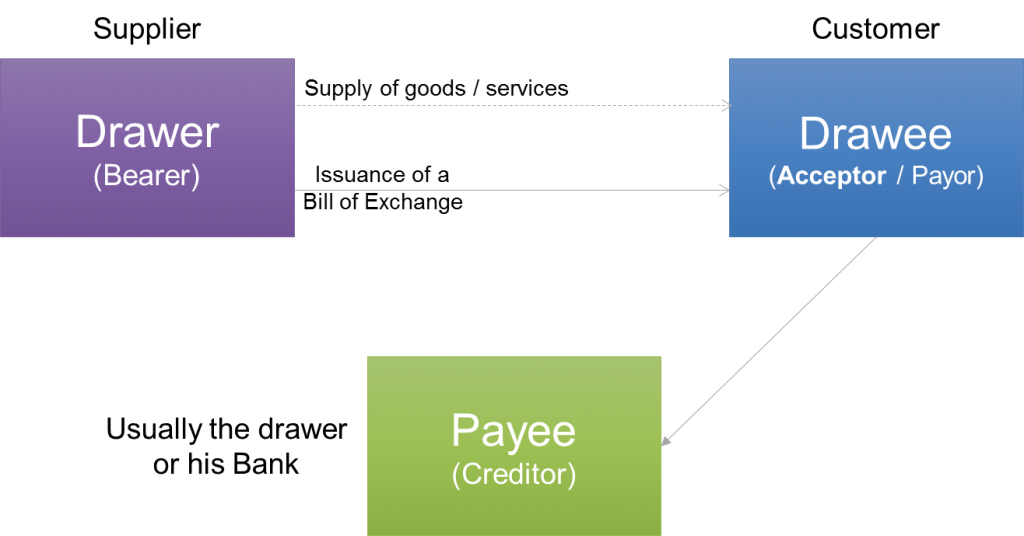
| Parties Involved in Bills of Exchange | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Drawer: The party who initiates the bill and demands payment from the drawee. The Drawee: The party who is obligated to make the payment stated on the bill. The Payee: The party who will receive the payment specified in the bill. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Advantages of Bills of Exchange | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bills of Exchange provide a secure payment method as they are governed by legal regulations and can be enforced in court if necessary. They enable businesses to extend credit to their customers, allowing for better cash flow management. Bills of Exchange are widely accepted internationally, facilitating trade across borders and reducing currency conversion risks. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bills of Exchange play a crucial role in international trade, providing a reliable and flexible method of payment. Understanding the key features and parties involved in bills of exchange is essential for businesses engaged in global transactions. By utilizing bills of exchange, businesses can enhance their financial operations and mitigate payment risks effectively. | ||
| 5 | ||