Autonomic Computing Presentation
| Introduction to Autonomic Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
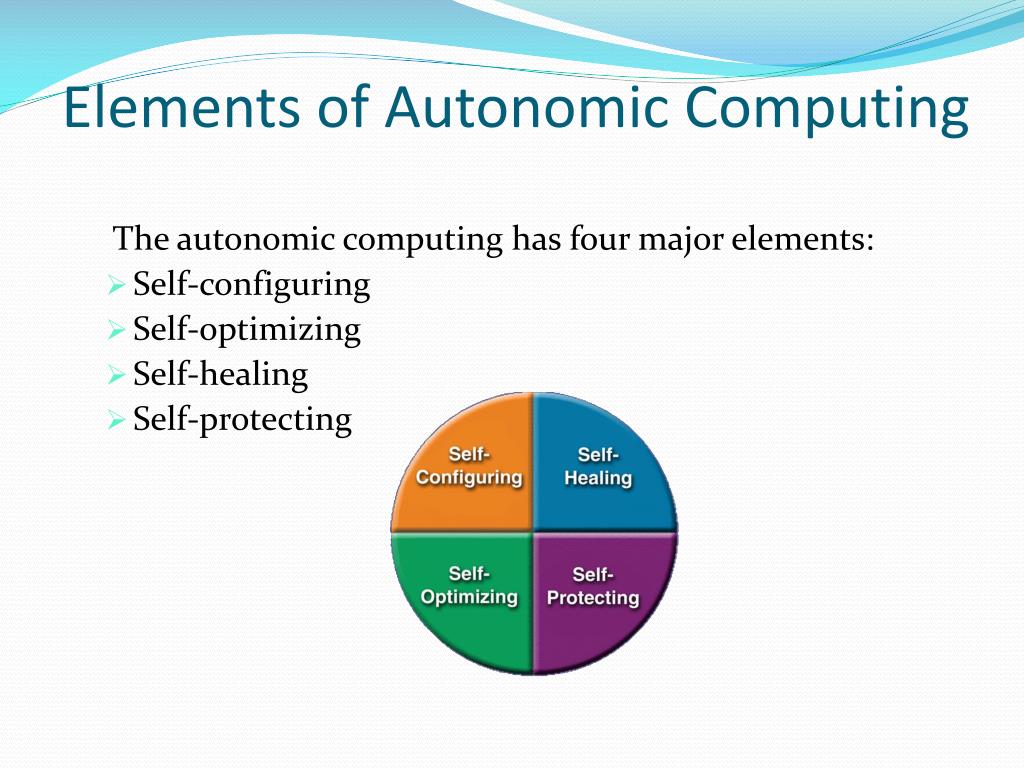
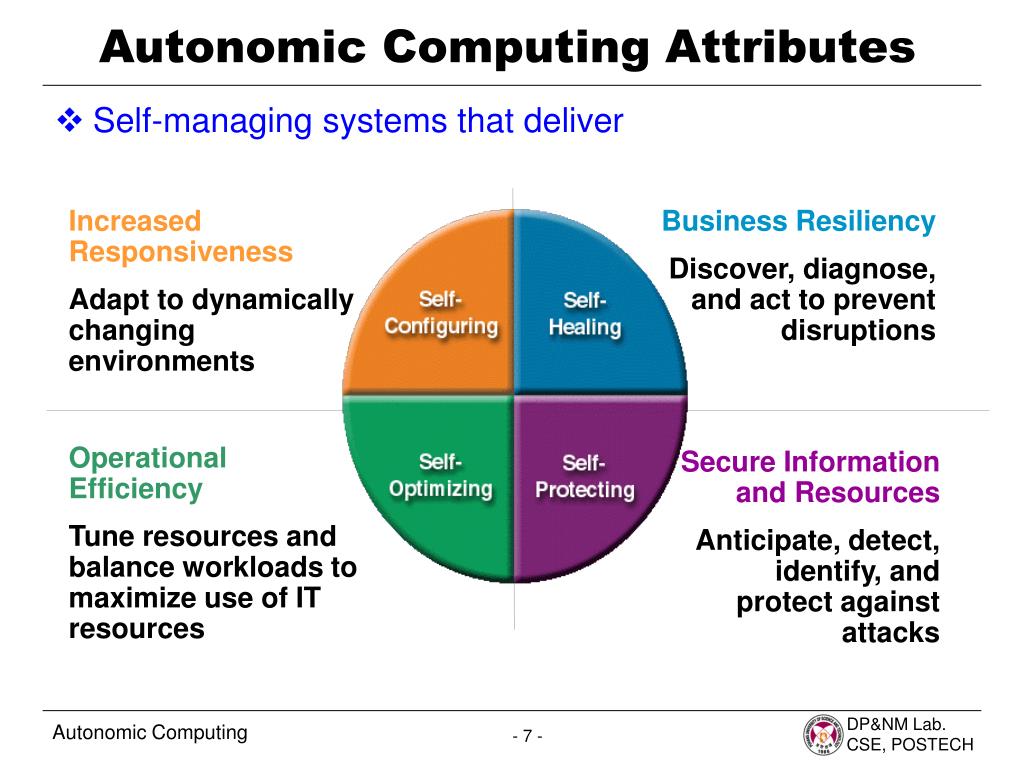
| Autonomic computing is a self-managing technology that aims to reduce the complexity of computing systems. It is inspired by the human autonomic nervous system, which regulates bodily functions without conscious effort. The goal of autonomic computing is to create systems that can self-configure, self-heal, self-optimize, and self-protect. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Key Principles of Autonomic Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Self-Configuration: Autonomic systems can automatically adapt to different environments and requirements. Self-Healing: Autonomic systems can detect and recover from failures without human intervention. Self-Optimization: Autonomic systems can continuously improve their performance and efficiency based on changing conditions. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Benefits of Autonomic Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Increased Reliability: Autonomic systems can detect and resolve issues before they become critical, minimizing downtime. Improved Scalability: Autonomic systems can dynamically adjust resources to meet changing demands, ensuring optimal performance. Reduced Complexity: Autonomic systems automate complex tasks, freeing up human resources to focus on higher-level tasks. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Applications of Autonomic Computing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Computing: Autonomic systems can optimize resource allocation and workload management in cloud environments. Internet of Things (IoT): Autonomic systems can manage and control a large number of interconnected devices without human intervention. Cybersecurity: Autonomic systems can detect and respond to security threats in real-time, enhancing overall system security. | ||
| 4 | ||