Air Pollution Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Air pollution is the contamination of the air with harmful substances. It can have serious health and environmental impacts. The main sources of air pollution include industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and burning of fossil fuels. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Types of Air Pollutants | ||
|---|---|---|
| Particulate Matter (PM): Tiny particles suspended in the air, can cause respiratory problems. Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Released from burning fossil fuels, contribute to smog and acid rain. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Emitted by vehicles and industrial processes, can lead to the formation of ground-level ozone. | ||
| 2 | ||
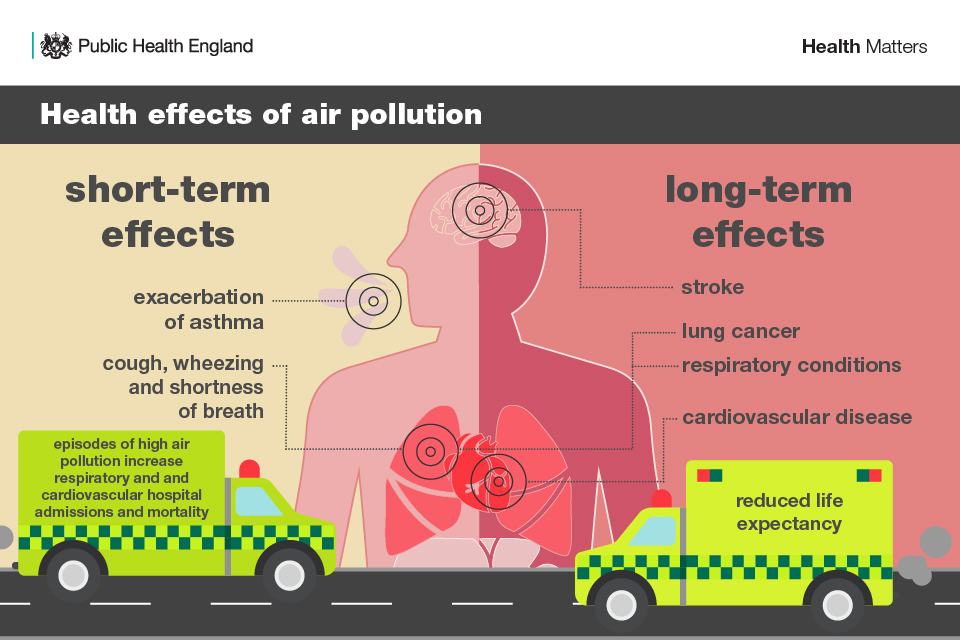
| Health Impacts of Air Pollution | ||
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory diseases: Long-term exposure to air pollution can lead to asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer. Cardiovascular issues: Air pollution increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Allergies and irritations: Pollutants can cause allergies, eye irritation, and skin problems. | ||
| 3 | ||
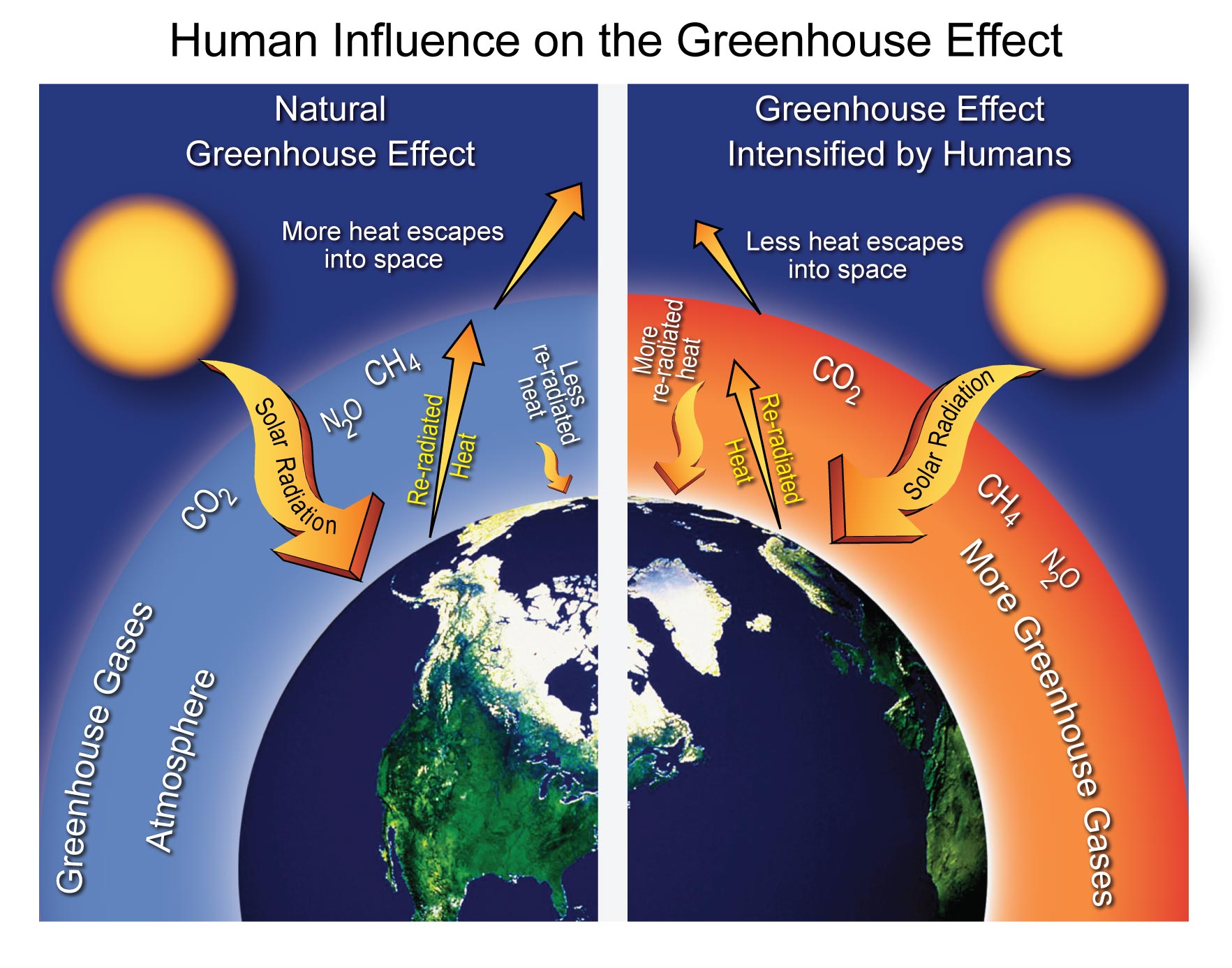
| Environmental Impacts of Air Pollution | ||
|---|---|---|
| Global warming: Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide contribute to climate change. Acid rain: Emissions of sulfur and nitrogen compounds cause acid rain, which damages ecosystems and buildings. Ozone depletion: Certain pollutants contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer, leading to increased UV radiation. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Air Quality Index (AQI) | ||
|---|---|---|
| AQI is a tool used to measure the quality of the air we breathe. It provides information about the current pollution levels and associated health risks. Different color-coded categories indicate the level of air pollution, from good to hazardous. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Solutions to Reduce Air Pollution | ||
|---|---|---|
| Use cleaner energy sources: Transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. Improve transportation: Promote electric vehicles, public transportation, and biking/ walking. Strict regulations: Enforce emission standards for industries and vehicles to reduce pollutants. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Individual Actions to Combat Air Pollution | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reduce vehicle use by carpooling or using public transportation. Conserve energy at home by using energy-efficient appliances and turning off lights when not in use. Support clean air initiatives and advocate for stricter environmental regulations. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Government Initiatives | ||
|---|---|---|
| Implement stricter emission standards for vehicles and industries. Invest in public transportation and infrastructure for electric vehicles. Support research and development of clean technologies. | ||
| 8 | ||
| International Efforts | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Paris Agreement: A global effort to combat climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The Clean Air Act: Legislation in the United States that aims to protect and improve air quality. International cooperation: Countries work together to address transboundary air pollution issues. | ||
| 9 | ||
| Conclusion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Air pollution is a significant global problem with severe health and environmental consequences. It requires collective efforts from governments, industries, and individuals to reduce pollution levels. By taking action and implementing sustainable solutions, we can improve air quality and protect future generations. | ||
| 10 | ||


Chart_US.png)




