Aeroponics Presentation
| Introduction | ||
|---|---|---|
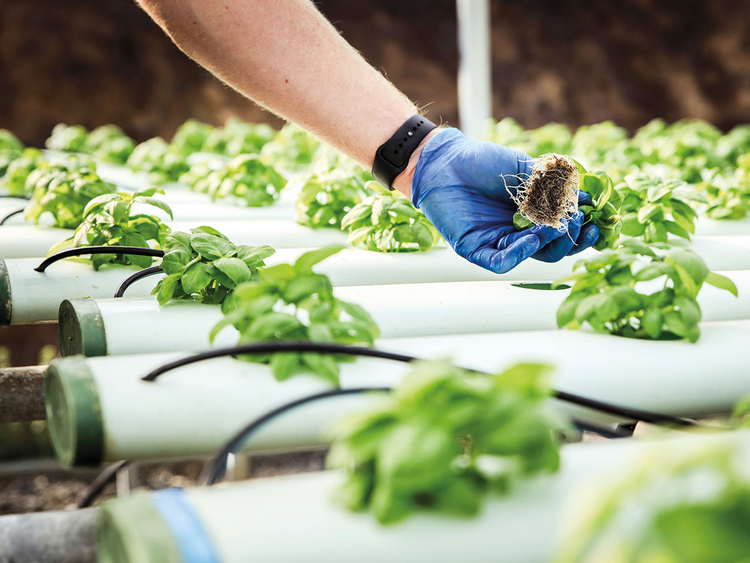
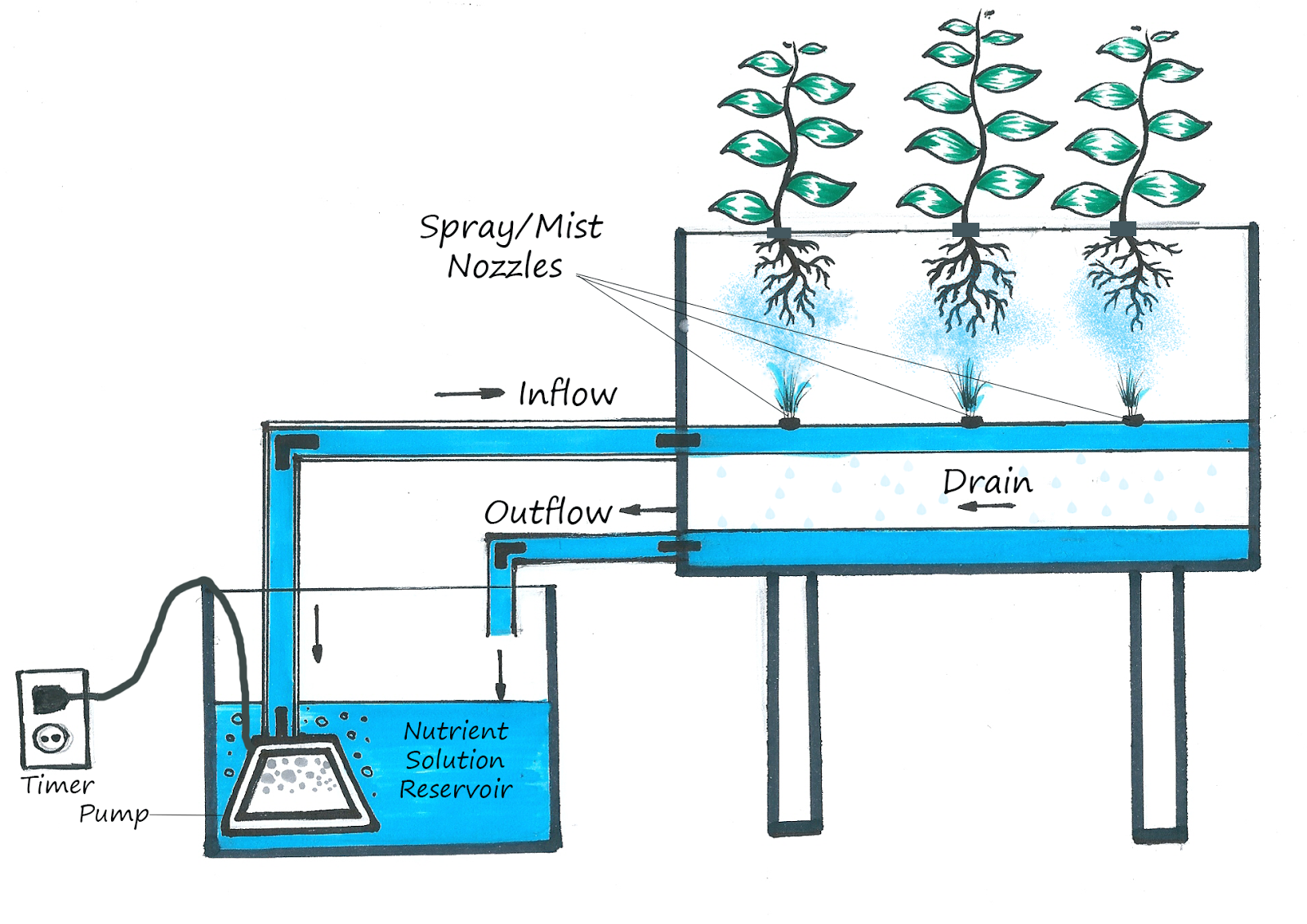
| Aeroponics is an innovative method of growing plants without soil. It involves suspending plant roots in a mist or air environment. This technique allows for efficient nutrient absorption and accelerated plant growth. | ||
| 1 | ||
| Benefits of Aeroponics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Increased crop yields - plants grow faster and produce more harvestable crops. Water conservation - aeroponics uses up to 90% less water compared to traditional farming methods. Space efficiency - vertical aeroponic systems require less land space for cultivation. | ||
| 2 | ||
| How Aeroponics Works | ||
|---|---|---|
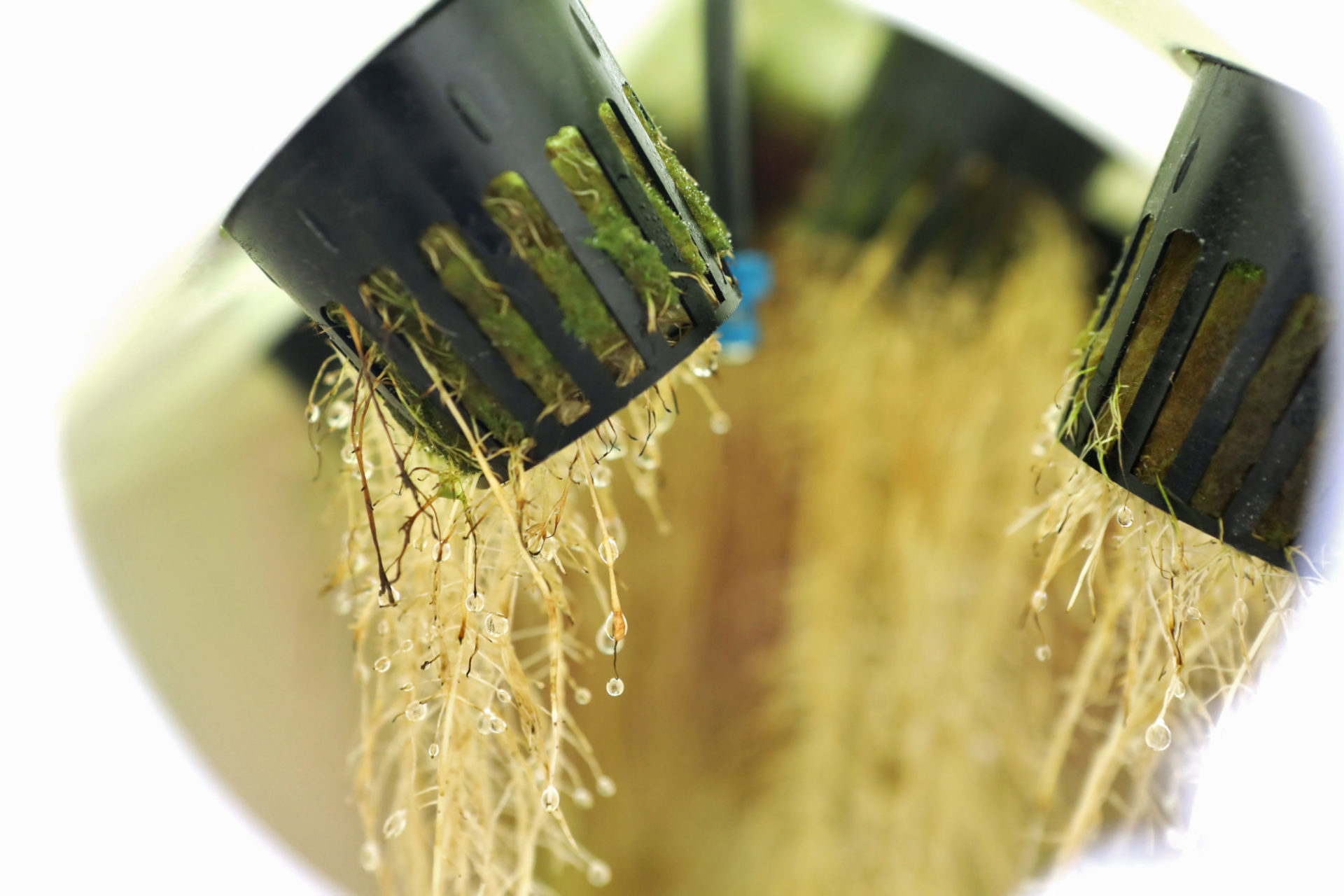
| Plants are suspended in a chamber or structure, with their roots exposed to a fine mist of nutrients and water. The mist is typically created using high-pressure pumps and specialized nozzles. The roots absorb the nutrients and water directly from the mist, promoting rapid growth and development. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Nutrient Delivery in Aeroponics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient solutions are mixed with water and sprayed onto the roots in the form of a fine mist. The mist provides an oxygen-rich environment for the roots, promoting healthy growth. Nutrient solutions can be customized to meet the specific needs of different plant species. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Types of Aeroponic Systems | ||
|---|---|---|
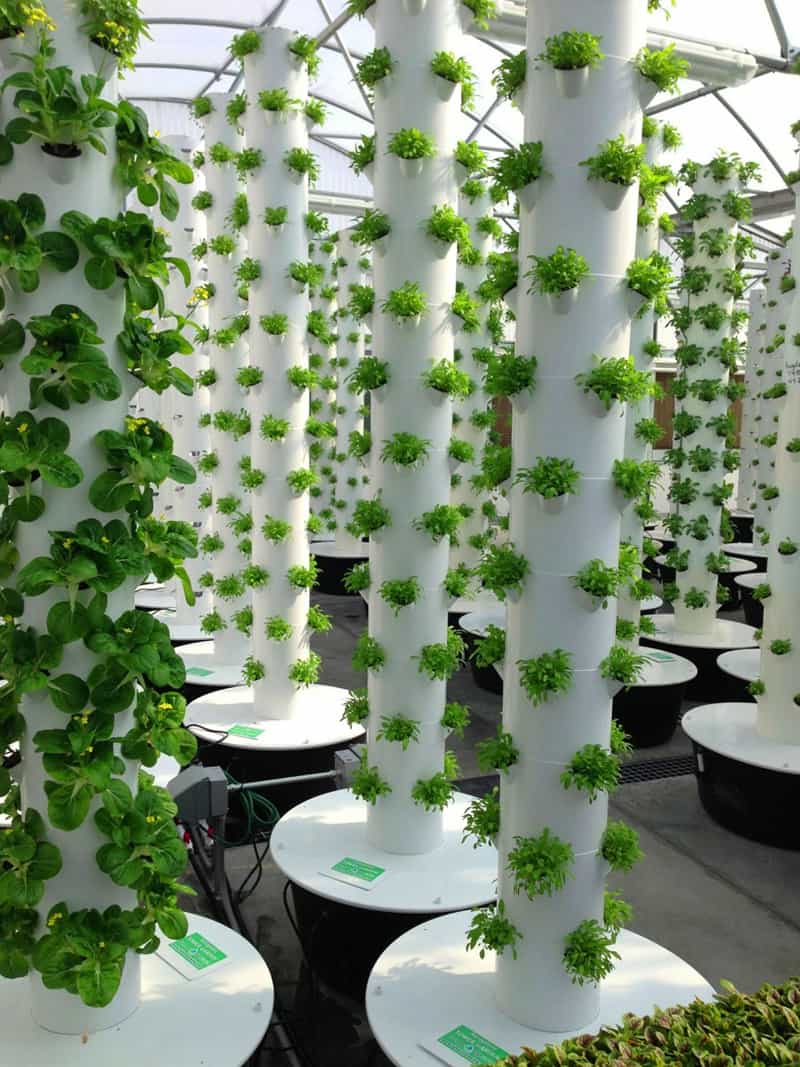
| Low-pressure systems - use low-pressure pumps to create mist for the plant roots. High-pressure systems - employ high-pressure pumps for a finer mist, ensuring better nutrient absorption. Vertical systems - utilize stacked layers of growing surfaces, maximizing space efficiency. | ||
| 5 | ||
| Plants Suitable for Aeroponics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Leafy greens - lettuce, spinach, kale, and herbs thrive in aeroponic systems. Tomatoes and peppers - these fruiting plants can also be grown successfully in aeroponics. Strawberries - the shallow root system of strawberries makes them suitable for aeroponic cultivation. | ||
| 6 | ||
| Challenges and Solutions in Aeroponics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Disease control - regular monitoring and proper hygiene practices help prevent the spread of diseases. Power outage - backup power systems can be implemented to ensure continuous misting during outages. Initial setup costs - although aeroponics requires initial investment, long-term savings on water and land space make it cost-effective. | ||
| 7 | ||
| Commercial Applications | ||
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse farming - aeroponics is a popular choice for greenhouse growers due to its space and water-saving benefits. Urban farming - vertical aeroponic systems enable food production in urban areas with limited space. Research purposes - aeroponics is widely used in plant research for studying root development and nutrient uptake. | ||
| 8 | ||
| Future of Aeroponics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Continued advancements in technology will lead to more efficient and affordable aeroponic systems. Increased adoption of aeroponics can contribute to sustainable agriculture and food security. Integration of automation and artificial intelligence will further enhance aeroponic farming practices. | ||
| 9 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| (Insert references here)... Your second bullet... Your third bullet... |  | |
| 10 | ||