A Unipolar World Presentation
| Introduction to A Unipolar World | ||
|---|---|---|
| A unipolar world refers to a global power structure where one country or entity dominates politically, economically, and militarily. The concept of a unipolar world gained attention after the collapse of the Soviet Union, leading to the United States becoming the sole superpower. A unipolar world has significant implications for global politics, security, and the balance of power. | ||
| 1 | ||
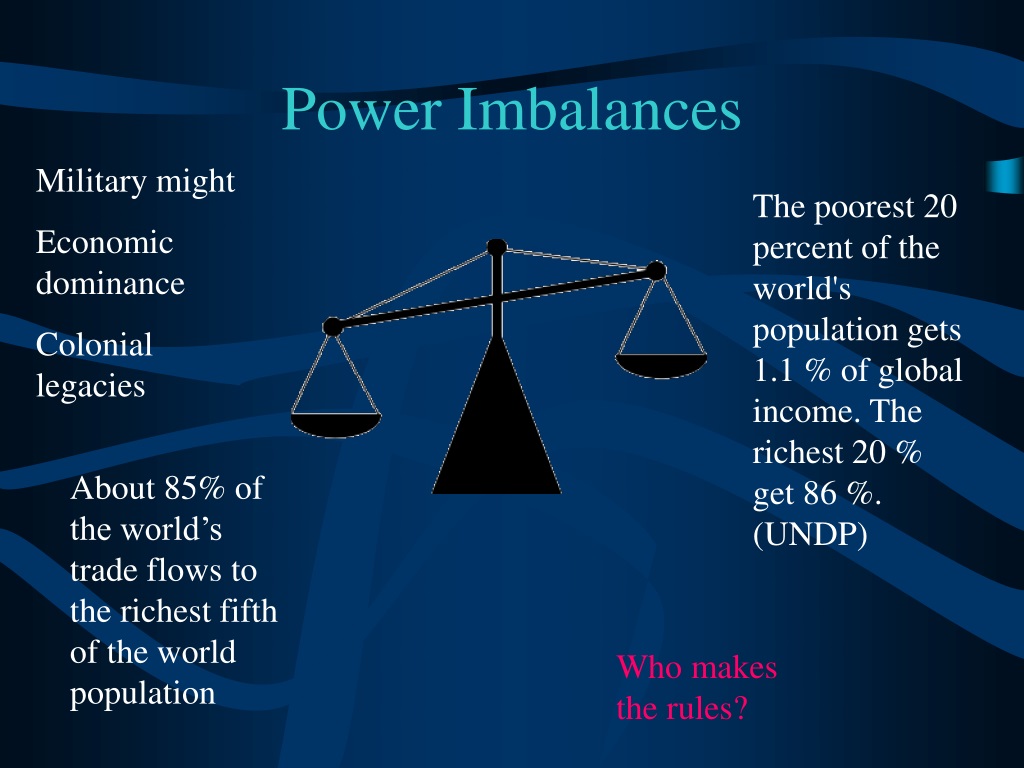
| Characteristics of a Unipolar World | ||
|---|---|---|
| The dominant power in a unipolar world sets the agenda and influences global decision-making processes. The dominant power enjoys economic advantages, such as control over global trade, resources, and financial institutions. In a unipolar world, the dominant power often has a significant military advantage, leading to a potential lack of deterrence and increased militarization. | ||
| 2 | ||
| Pros of a Unipolar World | ||
|---|---|---|
| Stability: A unipolar world can provide stability and deter conflicts due to the dominance of a single power. Economic Benefits: The dominant power can promote economic growth and facilitate global trade through its influence and control. Global Governance: A unipolar world allows for efficient decision-making and coordination in global governance, such as addressing climate change and international crises. | ||
| 3 | ||
| Cons of a Unipolar World | ||
|---|---|---|
| Power Imbalance: A unipolar world may lead to power imbalances, with the dominant power potentially exploiting weaker nations. Lack of Checks and Balances: Without a significant counterbalance, the dominant power may act unilaterally and disregard international norms and laws. Potential for Conflict: A unipolar world may increase tensions and conflicts as other rising powers challenge the dominant power's supremacy. | ||
| 4 | ||
| Challenges and Future Outlook | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rise of Multipolarity: The emergence of regional powers and shifting global dynamics challenge the concept of a unipolar world. Global Interdependence: Economic interdependence and transnational issues require collaborative approaches rather than a sole dominant power. Need for Cooperation: The future of global governance depends on cooperation among nations to address shared challenges and maintain stability. | ||
| 5 | ||
| References (download PPTX file for details) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Haass, R. N. (2008). The age of nonpolarity: ... Ikenberry, G. J. (2004). Illusions of empire:... Mearsheimer, J. J. (2001). The tragedy of gre... |  | |
| 6 | ||